Collaborative Consumption vs. Traditional Ownership in Digital Markets: A Comparative Analysis

Collaborative consumption vs. traditional ownership in digital markets sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
As we delve into the realms of collaborative consumption and traditional ownership in digital markets, we uncover a fascinating landscape that shapes consumer behavior and business practices.
Understanding Collaborative Consumption
Collaborative consumption in digital markets refers to the sharing or renting of goods, services, or resources among individuals, facilitated by online platforms. It is a shift away from traditional ownership towards a model focused on access and sharing.
Differences from Traditional Ownership
Collaborative consumption differs from traditional ownership in that it promotes the efficient use of resources by allowing multiple users to access the same item or service. Instead of owning a product outright, individuals can rent or share it as needed, reducing waste and promoting sustainability.
Popular Collaborative Consumption Platforms
- Uber: A ride-sharing platform that connects passengers with drivers who use their own vehicles.
- Airbnb: A platform that allows individuals to rent out their homes or properties to travelers.
- TaskRabbit: A service that connects people who need tasks done with individuals willing to complete them for a fee.
- ShareGrid: A platform for photographers and filmmakers to rent out equipment to other professionals in the industry.
Advantages of Collaborative Consumption
Collaborative consumption brings about various benefits for consumers, ranging from cost savings to environmental sustainability.
Cost Savings
- Sharing resources through collaborative consumption allows individuals to access goods and services at a fraction of the cost of traditional ownership.
- Renting or borrowing items instead of purchasing them outright can lead to significant savings over time.
- Platforms that facilitate collaborative consumption often offer competitive pricing and flexible payment options.
Environmental Impact
- Collaborative consumption promotes a more sustainable lifestyle by reducing overall consumption and waste generation.
- Sharing resources means fewer items are produced, leading to lower carbon emissions and resource depletion.
- By extending the lifespan of products through sharing and reuse, collaborative consumption helps lessen the environmental impact of manufacturing and disposal.
Success Stories
- Airbnb revolutionized the hospitality industry by allowing individuals to rent out their homes or spare rooms to travelers, creating a new income stream for hosts and offering unique accommodation options for guests.
- Zipcar introduced car-sharing as a convenient and cost-effective alternative to car ownership, reducing the need for private vehicles and promoting sustainable urban mobility.
- ThredUP transformed the fashion industry by enabling users to buy and sell secondhand clothing, reducing textile waste and promoting a circular economy in fashion.
Challenges of Collaborative Consumption

Collaborative consumption platforms face a variety of challenges that can impact their sustainability and growth. These challenges range from issues related to trust and security to regulatory hurdles that can hinder the operations of these businesses.
Trust and Security Concerns
- One of the major challenges faced by collaborative consumption platforms is building and maintaining trust among users. Since these platforms involve transactions between strangers, there is always a risk of fraud or misuse of services.
- Ensuring the security of personal information and financial transactions is crucial to gaining the confidence of users. Any breach of data can lead to a loss of trust and credibility for the platform.
- Implementing robust verification processes and user ratings/reviews systems can help alleviate some of these concerns, but it remains an ongoing challenge for many platforms.
Regulatory Hurdles
- Collaborative consumption businesses often face regulatory challenges due to the unconventional nature of their operations. Existing laws and regulations may not always apply to these new business models, creating uncertainty and legal risks.
- Issues such as taxation, insurance, liability, and compliance with local regulations can pose significant obstacles for collaborative consumption platforms. Navigating these legal complexities requires time, resources, and expertise.
- Furthermore, the lack of standardized regulations across different jurisdictions can also complicate the expansion of collaborative consumption businesses into new markets, requiring careful analysis and adaptation to local laws.
Traditional Ownership in Digital Markets
Traditional ownership models have long been the norm in various industries, where individuals or businesses own physical goods outright. This contrasts with collaborative consumption, where resources are shared among multiple users. However, with the rise of digital technologies, traditional ownership is evolving to adapt to the changing landscape.
Evolution of Traditional Ownership in the Digital Age
In the digital age, traditional ownership is undergoing a transformation as more companies embrace digital platforms to offer goods and services. For example, traditional brick-and-mortar retailers are expanding their reach by establishing online stores, allowing customers to purchase products digitally.
Industries Dominated by Traditional Ownership in Digital Markets
- Real Estate: The real estate industry still largely relies on traditional ownership models, where individuals purchase or rent properties for personal or investment purposes.
- Automotive: While car-sharing services are gaining popularity, many consumers still prefer to own their vehicles outright, leading to traditional ownership dominating the automotive sector.
- Luxury Goods: Industries like high-end fashion and luxury goods continue to thrive on traditional ownership, as consumers value exclusivity and ownership of luxury items.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences
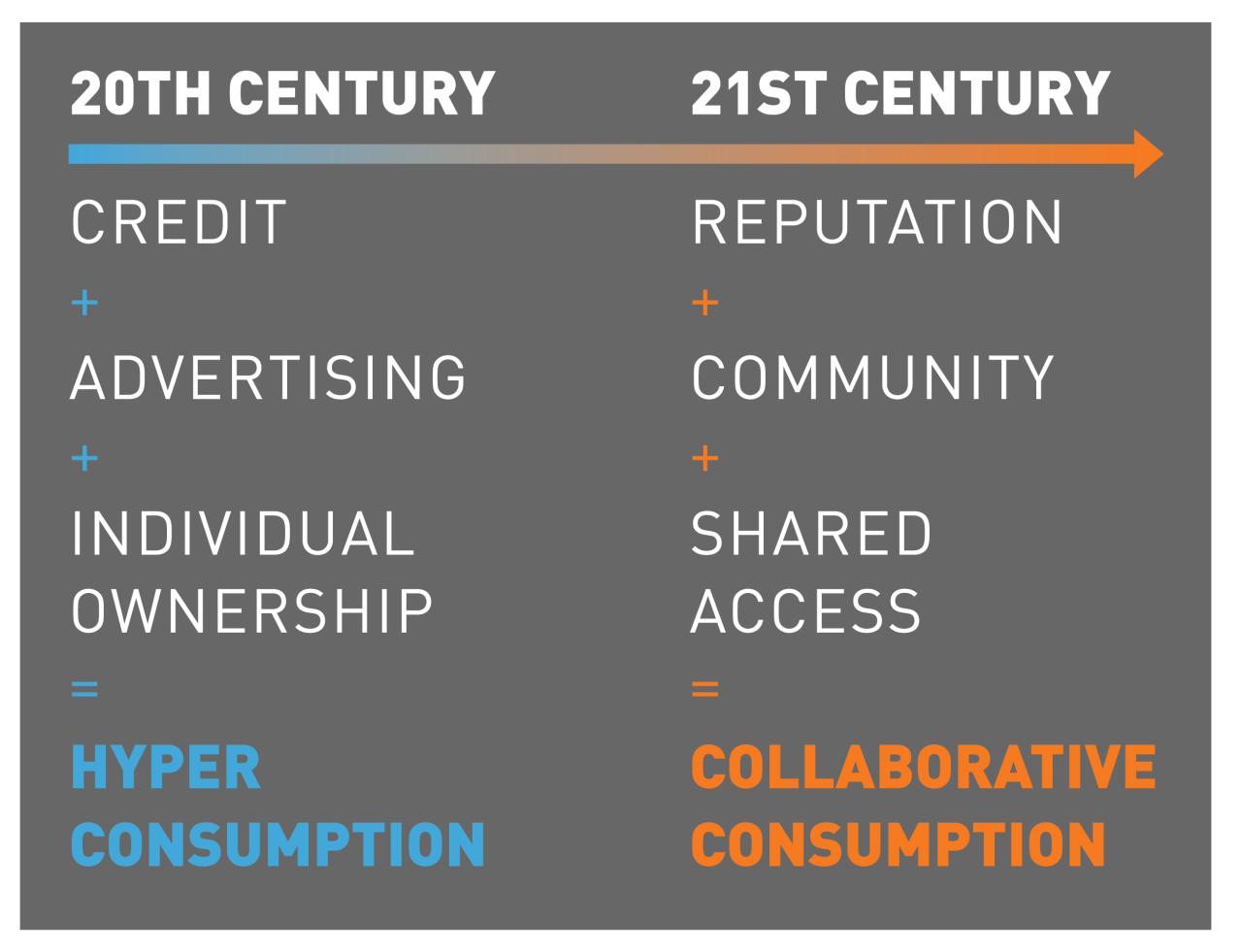
Consumer behavior is significantly influenced by the rise of collaborative consumption options in digital markets. This shift in consumer preferences can be attributed to various factors that drive individuals to choose collaborative consumption over traditional ownership. The role of trust and social connections also play a crucial part in shaping consumer preferences in this evolving market landscape.
Factors Influencing Consumer Choice
- Cost Efficiency: One of the primary reasons consumers opt for collaborative consumption is the cost savings it offers compared to traditional ownership. Shared resources and services allow individuals to access what they need without the burden of full ownership costs.
- Environmental Concerns: The growing awareness of sustainability and environmental impact has led consumers to prioritize sharing and reusing resources rather than accumulating more possessions. Collaborative consumption aligns with this shift towards eco-friendly practices.
- Convenience and Accessibility: The ease of access to a wide range of goods and services through digital platforms has made collaborative consumption a convenient choice for consumers. The ability to find and utilize resources quickly and efficiently appeals to individuals seeking convenience in their lifestyles.
Role of Trust and Social Connections
- Trust in Platforms: Consumers are more willing to engage in collaborative consumption when they trust the platforms facilitating these transactions. Positive reviews, secure payment systems, and transparent communication build trust among users and encourage participation in shared economies.
- Social Recommendations: Personal recommendations and social connections play a significant role in influencing consumer preferences for collaborative consumption. People are more likely to try sharing services or products recommended by friends or family members, reinforcing the importance of social connections in shaping consumer behavior.
- Community Building: Collaborative consumption fosters a sense of community among participants, creating networks of trust and cooperation. Consumers value the social connections and shared experiences that come with participating in collaborative consumption, further influencing their preferences in this market segment.
Concluding Remarks
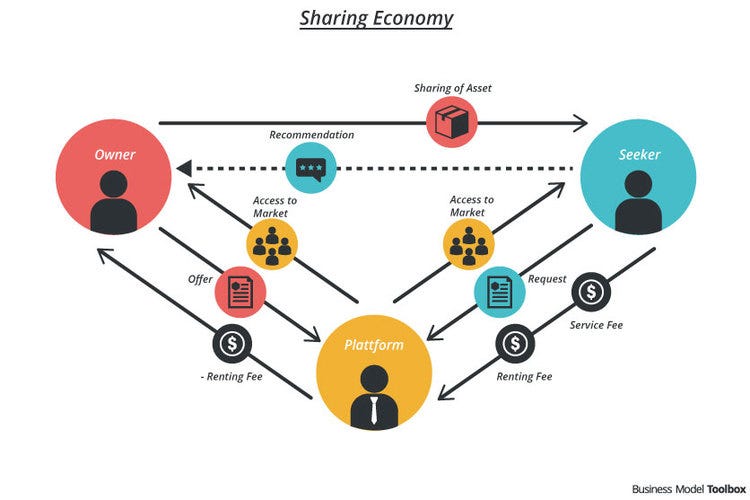
In conclusion, the juxtaposition of collaborative consumption and traditional ownership in digital markets highlights the evolving nature of consumer choices and market dynamics. It's a tale of innovation, sustainability, and changing paradigms that will continue to shape the future of commerce.
FAQ Guide
How does collaborative consumption differ from traditional ownership?
Collaborative consumption involves shared access to goods or services rather than individual ownership, promoting resource efficiency and community building.
What are the key benefits of collaborative consumption for consumers?
Consumers can save money, access a wider range of products or services, and contribute to a more sustainable economy through collaborative consumption.
What challenges do collaborative consumption platforms face?
Challenges include building trust among users, ensuring security of transactions, and navigating regulatory complexities in different markets.
How is traditional ownership evolving in the digital age?
Traditional ownership models are adapting to digital platforms through innovations like online marketplaces and subscription services, catering to changing consumer preferences.
What role do trust and social connections play in consumer preferences for collaborative consumption?
Trust and social connections are crucial in collaborative consumption, influencing consumers to engage in sharing economies based on familiarity and reliability within their networks.