Exploring the intricate connection between sleep and metabolism unveils a fascinating insight into how our body functions. Dive into the world of how sleep quality influences metabolic processes and discover the secrets behind achieving optimal health.
Delve deeper into the role of circadian rhythm, hormonal regulation, and the impact of sleep duration on metabolic rate to gain a comprehensive understanding of how these factors shape our overall well-being.
How Sleep Quality Impacts Metabolism
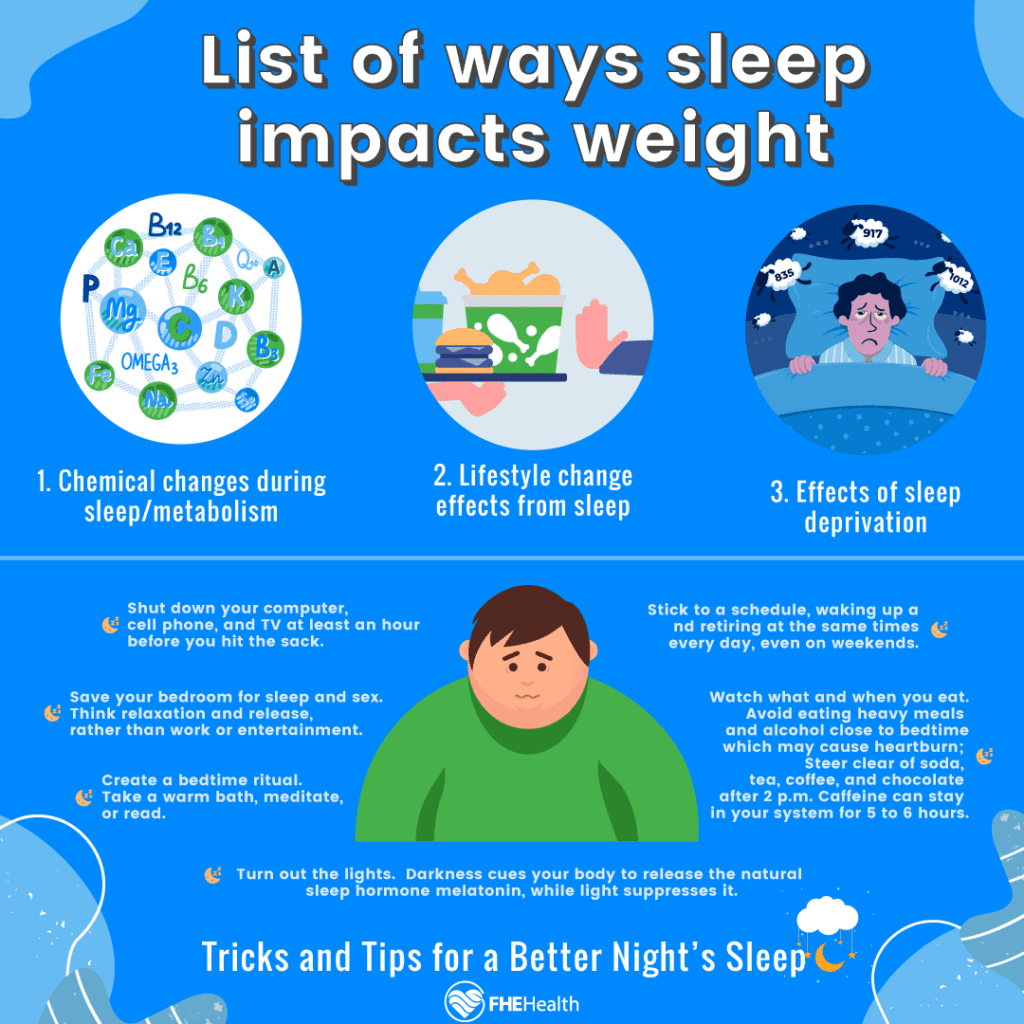
Sleep quality plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and overall health. When we don’t get enough good quality sleep, it can have various negative impacts on our metabolic processes, leading to potential health issues.
Effects of Poor Sleep on Metabolic Processes
Poor sleep quality can disrupt the balance of hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, such as leptin and ghrelin. This imbalance can lead to increased feelings of hunger and cravings for unhealthy foods, ultimately contributing to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction.
Inadequate sleep also impairs glucose metabolism, leading to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.Research has shown that chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of metabolic disorders such as obesity, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome.
The link between poor sleep and metabolic health is well-established, highlighting the importance of prioritizing good sleep habits for overall well-being.
Getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night is essential for maintaining a healthy metabolism and reducing the risk of metabolic disorders.
The Role of Circadian Rhythm in Metabolism
Sleep and metabolism are closely intertwined, with the body’s internal clock, known as the circadian rhythm, playing a crucial role in regulating metabolic processes. This internal clock helps coordinate various physiological functions, including metabolism, in a 24-hour cycle.The circadian rhythm influences metabolism by regulating the timing of key metabolic processes such as glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, and energy expenditure.
For example, the body’s ability to efficiently metabolize glucose is highest during the day when we are active and decreases during the night when we are at rest.Disruptions in the circadian rhythm, such as irregular sleep patterns, shift work, jet lag, or exposure to artificial light at night, can have a significant impact on metabolic functions.
Studies have shown that individuals with disrupted circadian rhythms are more likely to develop metabolic disorders such as obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes.
Optimizing Circadian Rhythm for Metabolic Health
- Avoid exposure to bright light at night: Limit exposure to artificial light at night, especially blue light from electronic devices, to help maintain a healthy circadian rhythm.
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promote metabolic health.
- Follow a healthy diet: Eating meals at consistent times throughout the day can help synchronize your metabolism with your circadian rhythm.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise can help regulate your circadian rhythm and improve metabolic function.
- Create a bedtime routine: Establishing a relaxing bedtime routine can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep, supporting a healthy circadian rhythm.
Hormonal Regulation During Sleep and Metabolism
Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating various hormones that impact metabolism. Hormones like cortisol, insulin, and leptin are key players in this intricate process, influencing how our bodies process energy and store fat.
Role of Cortisol in Metabolism
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, is involved in regulating metabolism by managing glucose levels in the body. During sleep, cortisol levels typically decrease, allowing the body to rest and recover. However, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which may disrupt metabolic processes and contribute to weight gain.
Importance of Insulin in Metabolism
Insulin is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels and promoting the storage of nutrients. Adequate sleep is crucial for insulin sensitivity, as sleep deprivation can lead to insulin resistance, where cells do not respond effectively to insulin. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels and an increased risk of metabolic disorders like diabetes.
Role of Leptin in Regulating Appetite
Leptin is a hormone that signals to the brain when the body has had enough food and helps regulate energy balance. During sleep, leptin levels typically rise, promoting feelings of fullness and reducing appetite. Inadequate sleep can disrupt this balance, leading to lower levels of leptin and increased hunger cravings, which can impact metabolism and contribute to weight gain.
Optimizing Hormone Regulation for Metabolic Health
To optimize hormone regulation for better metabolic function, prioritizing quality sleep is essential. Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can help support healthy hormone balance. Additionally, managing stress levels through relaxation techniques and regular exercise can also positively impact hormone regulation and metabolic processes.
Sleep Duration and Metabolic Rate
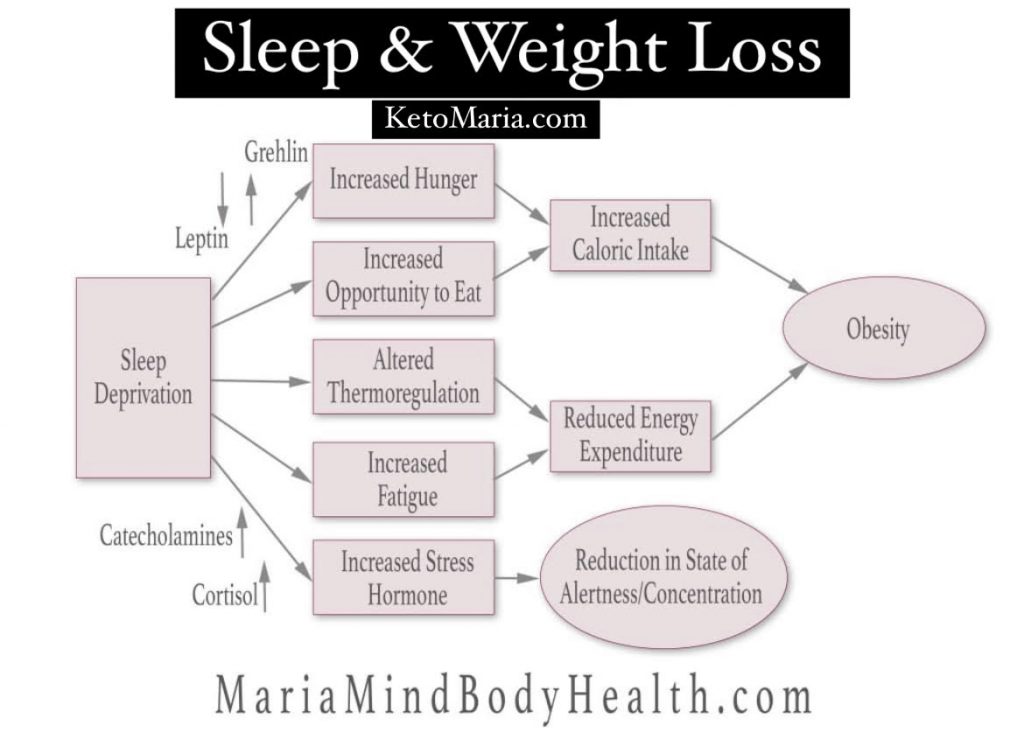
Research has shown a clear link between sleep duration and metabolic rate, highlighting the importance of getting the right amount of sleep for optimal metabolic function.
Effects of Insufficient Sleep Duration on Metabolism
- Insufficient sleep, typically defined as less than 7-8 hours per night, can lead to metabolic dysregulation.
- Studies have shown that inadequate sleep duration is associated with increased hunger hormones like ghrelin and decreased satiety hormones like leptin, leading to overeating and weight gain.
- Furthermore, insufficient sleep can disrupt blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity, increasing the risk of developing metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes.
Effects of Excessive Sleep Duration on Metabolism
- On the other hand, excessive sleep, usually more than 9-10 hours per night, has also been linked to negative metabolic effects.
- Research suggests that prolonged sleep duration may be associated with higher levels of inflammation markers and insulin resistance, contributing to metabolic abnormalities.
- Additionally, oversleeping can disrupt the body’s natural circadian rhythm, impacting metabolic processes and energy balance.
Recommendations for Optimal Sleep Duration
- For most adults, aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night is recommended to support a healthy metabolic rate.
- Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing sleep environment can help improve sleep quality and duration.
- Avoiding caffeine and electronic devices close to bedtime, as well as engaging in regular physical activity, can also promote better sleep habits and metabolic health.
Closure

As we conclude our exploration of how sleep affects metabolism, we are reminded of the profound impact that a good night’s rest can have on our body’s metabolic functions. By prioritizing quality sleep and understanding its relationship with metabolism, we pave the way towards a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
Top FAQs
Does poor sleep really affect metabolism?
Poor sleep can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to imbalances in hormones that regulate metabolism such as cortisol and insulin.
Can optimizing circadian rhythm improve metabolic health?
Yes, aligning your circadian rhythm with natural light-dark cycles can positively impact metabolic functions and overall health.
How does hormone regulation during sleep influence metabolism?
Hormones like leptin play a crucial role in regulating appetite and energy expenditure during sleep, directly impacting metabolic processes.
Is there an ideal sleep duration for maintaining a healthy metabolic rate?
Research suggests that getting 7-9 hours of sleep per night is optimal for supporting a healthy metabolic rate.