How the Share Economy is Disrupting Traditional Business Models

In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, the share economy is making waves by challenging traditional business models. This shift towards collaborative consumption is reshaping industries and redefining the way we think about ownership and services. As we delve into the impact of the share economy on businesses, it becomes evident that adaptability and innovation are key to survival in this dynamic environment.
As we explore the different facets of this transformation, it becomes clear that traditional notions of ownership and consumption are being redefined in profound ways.
Table of Contents
ToggleOverview of the sharing economy

The sharing economy, also known as the collaborative economy, is a socio-economic system built around the sharing of resources, often facilitated by technology platforms. Unlike traditional business models where ownership is emphasized, the sharing economy focuses on access and sharing resources between individuals or groups.
Popular Sharing Economy Platforms
- Uber: Disrupting the transportation industry by connecting riders with drivers through a mobile app, offering a more convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional taxi services.
- Airbnb: Revolutionizing the hospitality industry by allowing individuals to rent out their homes or properties to travelers, providing unique accommodation options and experiences.
- TaskRabbit: Changing the way people outsource tasks by connecting users with skilled individuals who can help with various chores and errands.
Benefits and Challenges
The sharing economy model offers several advantages, such as increased efficiency, cost savings, and environmental sustainability through resource optimization. However, it also presents challenges like regulatory issues, trust and safety concerns, and potential exploitation of workers in the gig economy.
Role of Technology
Technology has played a significant role in the growth of the sharing economy, enabling platforms to connect users seamlessly, facilitate transactions, and build trust through user reviews and ratings. The use of mobile apps and online platforms has made it easier for individuals to participate in sharing resources and services.
Impact on traditional businesses
Traditional businesses are facing significant challenges due to the rise of the sharing economy. This shift in consumer behavior towards sharing services has disrupted many industries and forced traditional businesses to rethink their strategies to stay competitive.
Cost Structures
- Traditional businesses often have higher fixed costs, such as owning or leasing physical storefronts, maintaining inventory, and managing employees.
- Sharing economy platforms operate on a more flexible cost structure, where they utilize existing resources more efficiently without the burden of owning physical assets.
- As a result, sharing economy platforms can offer services at lower prices, attracting cost-conscious consumers away from traditional businesses.
Consumer Preferences
- Consumers are increasingly valuing experiences over ownership, leading to a shift towards sharing economy services that provide access to goods and services without the commitment of ownership.
- Millennials, in particular, are driving this trend as they prioritize convenience, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness in their consumption habits.
- This change in consumer preferences has forced traditional businesses to adapt their offerings to meet the demand for more flexible and on-demand services.
Competing Strategies
- Traditional businesses can embrace the sharing economy model by incorporating elements of sharing or subscription services into their business models.
- They can also focus on enhancing customer experience, offering personalized services, and leveraging technology to streamline operations and compete with sharing economy platforms.
- Collaborating with sharing economy platforms or investing in digital marketing and online presence can help traditional businesses reach new customers and stay relevant in a rapidly evolving market.
Disruption in transportation and accommodation sectors
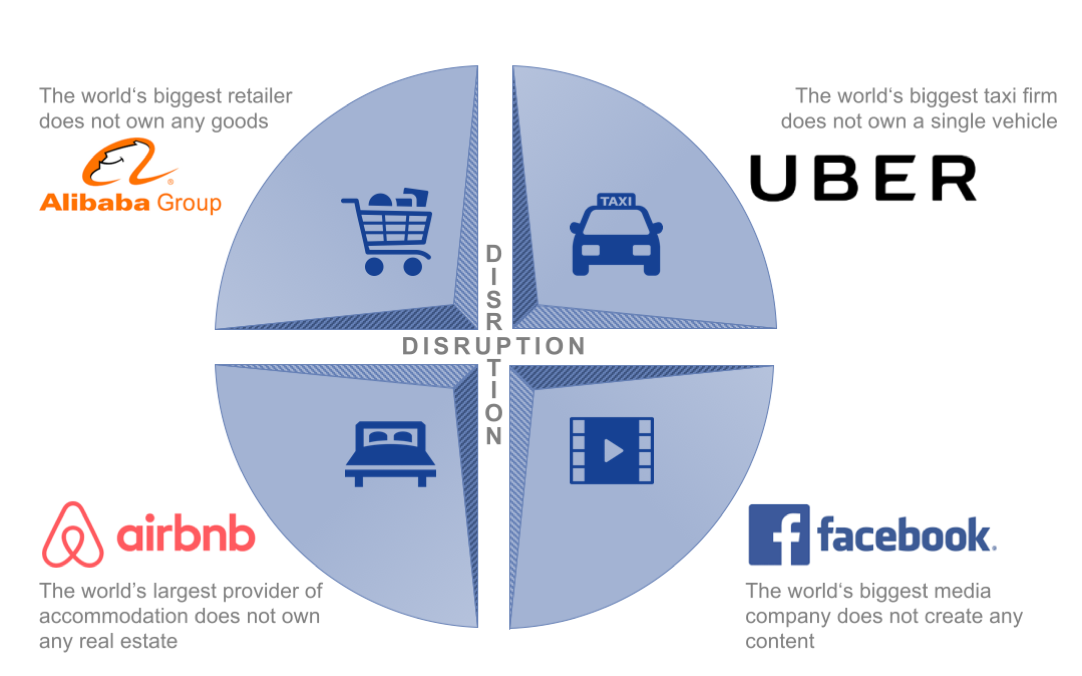
The rise of the sharing economy has significantly disrupted the traditional business models in the transportation and accommodation sectors. Companies like Uber and Airbnb have revolutionized the way people travel and find lodging, leading to a wave of innovation and challenges in these industries.
Uber: Transforming Transportation
Uber's innovative business model of connecting riders with drivers through a mobile app has completely transformed the transportation industry. By leveraging existing resources (personal vehicles) and providing a convenient and cost-effective alternative to traditional taxis, Uber has become a dominant player in the market.
This has led to a shift in consumer preferences and forced traditional taxi companies to adapt or risk becoming obsolete.
Airbnb: Disrupting Accommodation
Airbnb's platform allowing homeowners to rent out their properties to travelers has disrupted the accommodation sector. By offering a wide range of options at varying price points, Airbnb has provided travelers with more choices and flexibility compared to traditional hotels.
This has challenged the hospitality industry to rethink its approach and cater to changing consumer demands.
Regulatory Challenges
One of the main challenges faced by sharing economy companies like Uber and Airbnb is navigating the regulatory landscape. Traditional businesses in transportation and accommodation are subject to strict regulations regarding licensing, safety standards, and taxation, which can create barriers for sharing economy platforms.
This has led to legal battles and debates over how to regulate these innovative business models while ensuring consumer protection.
Long-term Implications
The disruption caused by companies like Uber and Airbnb in the transportation and accommodation sectors is likely to have long-term implications for traditional businesses. As the sharing economy continues to grow and evolve, traditional transportation companies and hotels will need to adapt or risk losing market share.
This shift towards more decentralized and customer-centric models could lead to a more competitive and diverse marketplace, ultimately benefiting consumers through increased choice and lower prices.
Socio-economic implications
The sharing economy has significant socio-economic implications that are reshaping employment patterns, consumer behavior, trust systems, and sustainability efforts.
Employment patterns
- The sharing economy has led to the rise of freelance and gig economy workers who can now access flexible job opportunities through platforms like Uber, Airbnb, and TaskRabbit.
- This shift towards independent work has both positive and negative impacts, providing individuals with autonomy and flexibility but also raising concerns about job security and benefits.
- Traditional industries are adapting to this new model by offering more flexible work arrangements to attract and retain talent.
Consumer behavior and ownership trends
- Consumers are increasingly valuing access over ownership, preferring to rent or share goods and services rather than buy them outright.
- This shift is driven by cost savings, convenience, and a growing awareness of the environmental impact of overconsumption.
- Companies are responding to this trend by offering subscription-based services and shared ownership models to meet the changing preferences of their customers.
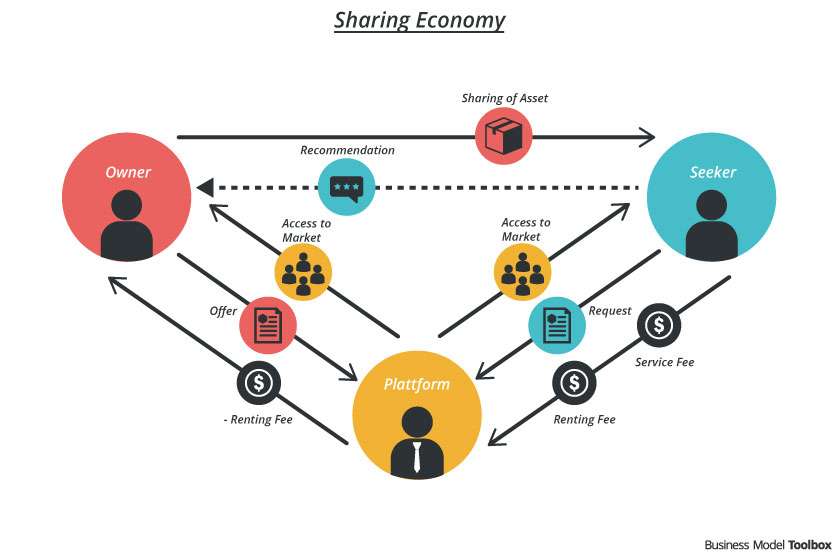
Trust and reputation systems
- Trust and reputation systems play a crucial role in the sharing economy, as they enable users to assess the reliability and credibility of service providers and peers.
- Platforms like Airbnb and Uber rely on user reviews and ratings to build trust among their communities and ensure quality experiences.
- These systems help to mitigate risks associated with sharing economy transactions and foster a sense of accountability among participants.
Contribution to sustainability and resource optimization
- The sharing economy promotes resource efficiency by maximizing the use of existing assets and reducing waste through shared consumption.
- By enabling the reuse and repurposing of goods and services, the sharing economy contributes to a more sustainable and circular economy model.
- Businesses in the sharing economy are increasingly focused on environmental sustainability and are implementing practices to minimize their carbon footprint and promote responsible consumption.
Epilogue
As we wrap up our discussion on how the share economy is disrupting traditional business models, it's evident that the landscape of commerce is undergoing a significant paradigm shift. With technology driving this change, businesses must embrace innovation and adapt to the evolving consumer preferences to thrive in this new era of collaborative consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some popular sharing economy platforms disrupting various industries?
Some examples include Uber in transportation, Airbnb in accommodation, and TaskRabbit in services.
How can traditional businesses compete in the sharing economy landscape?
Traditional businesses can adapt by embracing technology, offering unique value propositions, and focusing on customer experience to compete effectively.
What role do trust and reputation systems play in the sharing economy?
Trust and reputation systems are crucial in the share economy as they build credibility and establish reliability among users, fostering a sense of community and accountability.
Related posts
Why Millennials Embrace the Share Economy in 2025: A Look into the Future
Top digital platforms leading the global share economy: A Comprehensive Guide
Collaborative Consumption vs. Traditional Ownership in Digital Markets: A Comparative Analysis
Most popular
- Monetizing underused assets in the digital share economy: Unlocking Hidden Value

- The future of job creation in the platform share economy: Shaping Opportunities in a Digital Era

- Global Challenges of Trust in Digital Share Economies: Navigating the Digital Landscape
- How Digital Platforms Enable Equitable Value Sharing: Exploring Mechanisms and User Empowerment

- How freelancers benefit from the global share economy: A Comprehensive Guide