Low-carb vs metabolic diet comparison sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality. Exploring the nuances of these two popular diets sheds light on their impact on weight loss, health, and overall well-being.
Low-carb Diet Overview
A low-carb diet is a dietary approach that focuses on reducing the intake of carbohydrates, primarily found in foods like bread, pasta, and sugary treats. Instead, the emphasis is placed on consuming foods that are high in protein, healthy fats, and non-starchy vegetables.
Common Foods on a Low-carb Diet
- Lean meats such as chicken, turkey, and beef
- Fatty fish like salmon and mackerel
- Eggs
- Nuts and seeds
- Leafy greens and other non-starchy vegetables
- Healthy fats such as avocado, olive oil, and coconut oil
Potential Benefits of a Low-carb Diet
Following a low-carb diet may offer several benefits, including:
- Weight loss: By reducing carb intake, the body is encouraged to burn stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss.
- Improved blood sugar levels: Lower carb consumption can help stabilize blood sugar levels, which is beneficial for individuals with diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Reduced cravings: By minimizing spikes in blood sugar, a low-carb diet can help control cravings and promote better appetite regulation.
- Increased energy: Some individuals report feeling more energized and focused when following a low-carb eating plan.
Metabolic Diet Overview
A metabolic diet focuses on optimizing the body’s metabolism to promote efficient energy production and overall well-being. Unlike a low-carb diet that primarily restricts carbohydrate intake, a metabolic diet takes a more holistic approach by considering the impact of various nutrients on metabolism.
Recommended Foods
- Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes
- Healthy fats like avocado, nuts, seeds, and olive oil
- Complex carbohydrates from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables
- Dairy products for calcium and probiotics
- Foods rich in antioxidants like berries, spinach, and kale
Impact on Metabolism and Energy Levels
A metabolic diet helps regulate blood sugar levels, which can prevent spikes and crashes that lead to fatigue. By including a balance of macronutrients and micronutrients, this diet supports metabolic functions such as digestion, absorption, and energy production. The combination of nutrients also aids in maintaining muscle mass and promoting a healthy metabolism, ultimately leading to sustained energy levels throughout the day.
Nutritional Differences
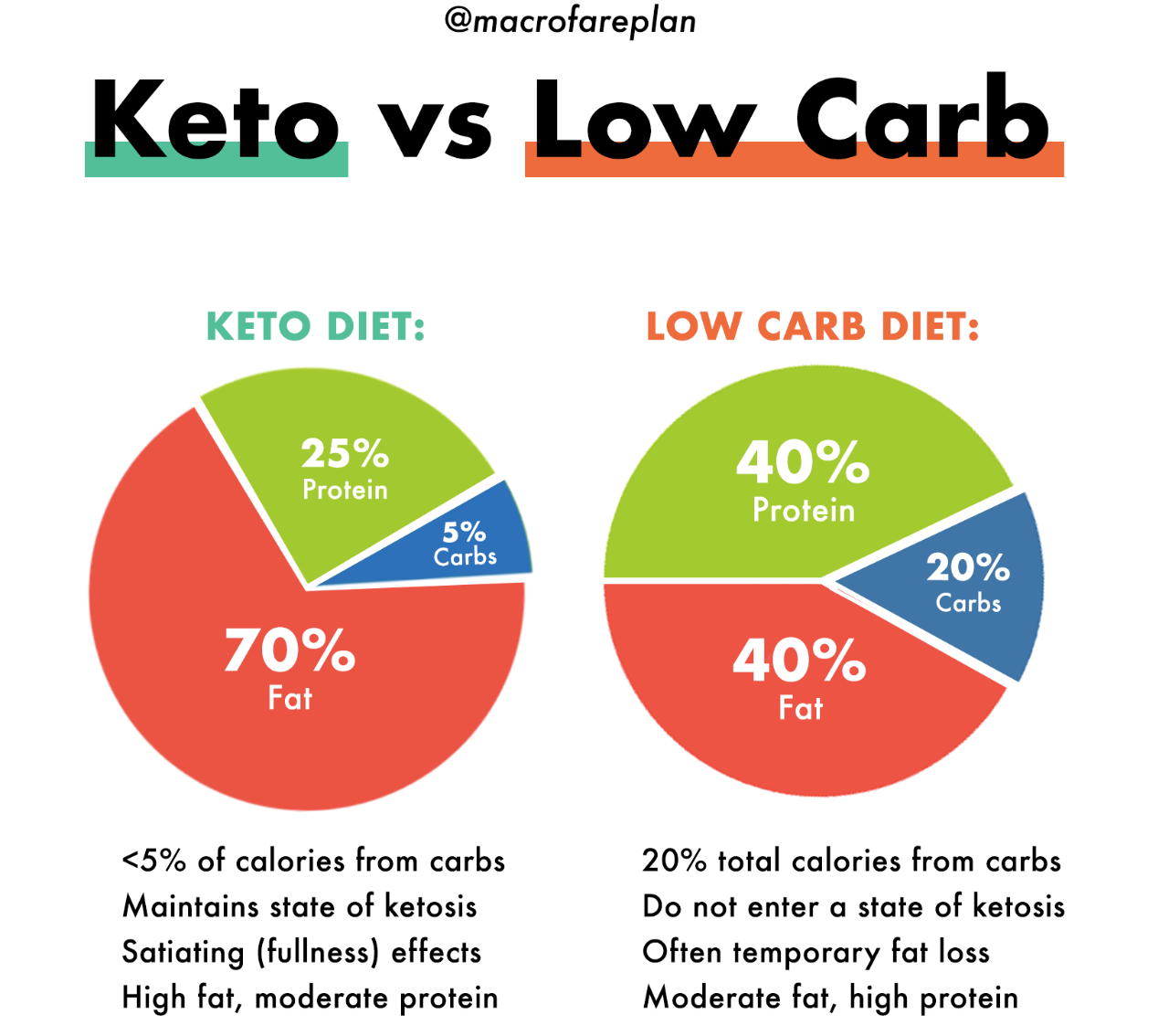
In comparing the macronutrient composition of a low-carb diet to a metabolic diet, it’s important to note the key differences in how each diet affects insulin levels, blood sugar regulation, and the role of ketosis.
Macronutrient Composition
- A low-carb diet typically consists of high fat, moderate protein, and very low carb intake, usually below 50 grams per day. This composition aims to shift the body’s energy source from carbohydrates to fats.
- On the other hand, a metabolic diet focuses on balanced macronutrient ratios, including a mix of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. The emphasis is on utilizing macronutrients efficiently to optimize metabolism.
Insulin Levels and Blood Sugar Regulation
- In a low-carb diet, the reduced intake of carbohydrates leads to lower insulin levels in the blood. This can result in improved blood sugar regulation and decreased risk of insulin resistance.
- Contrastingly, a metabolic diet aims to maintain stable insulin levels by moderating carbohydrate intake and pairing it with protein and fats to prevent spikes and crashes in blood sugar.
Role of Ketosis
- A key feature of a low-carb diet is the induction of ketosis, where the body produces ketones as an alternative fuel source in the absence of carbs. This metabolic state is associated with fat loss and increased energy levels.
- Conversely, a metabolic diet does not necessarily induce ketosis but focuses on optimizing the body’s metabolism through balanced macronutrient intake and efficient energy utilization.
Health Implications

Following a specific diet plan can have various implications on one’s health in the long run. Let’s delve into the potential effects of both low-carb and metabolic diets on overall well-being.
Long-Term Effects of Low-Carb Diet
- Weight Loss: Low-carb diets are often effective for short-term weight loss due to reduced calorie intake. However, long-term sustainability may vary.
- Heart Health: Some studies suggest that low-carb diets may improve heart health markers, such as lowering triglycerides and increasing HDL cholesterol.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Restricting carbohydrates can lead to deficiencies in essential nutrients like fiber, vitamins, and minerals if not carefully planned.
- Metabolic Adaptation: Prolonged low-carb intake may alter metabolic processes, potentially affecting energy levels and overall metabolism.
Benefits of Metabolic Diet
A metabolic diet focuses on improving overall health by optimizing metabolic function and hormonal balance. Here are some potential benefits:
- Stable Blood Sugar: By balancing macronutrient ratios and meal timing, a metabolic diet may help regulate blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Sustained Energy: Properly fueling the body with nutrients tailored to individual metabolism can provide sustained energy throughout the day.
- Hormonal Regulation: The metabolic diet aims to support hormonal balance, which can have a positive impact on various bodily functions, such as metabolism, mood, and sleep.
Risks and Considerations
- Low-Carb Diet Risks: Potential risks of long-term low-carb diets include increased risk of nutrient deficiencies, constipation, and potential negative impact on gut health.
- Metabolic Diet Considerations: While a metabolic diet can support overall health, individualized approaches are crucial, as metabolic needs vary among individuals.
End of Discussion

In conclusion, the comparison between low-carb and metabolic diets reveals a fascinating journey through nutrition and health. Understanding the differences and benefits of each diet empowers individuals to make informed choices for their well-being.
FAQs
What is the main difference between a low-carb diet and a metabolic diet?
A low-carb diet focuses on reducing carbohydrate intake, while a metabolic diet emphasizes optimizing metabolism through specific food choices and meal timings.
Do low-carb diets always lead to ketosis?
Not necessarily. While low-carb diets can induce ketosis in some individuals, it depends on the level of carbohydrate restriction and other factors.
Can a metabolic diet be considered a low-carb diet as well?
Although some aspects of a metabolic diet may align with a low-carb approach, they are distinct in their emphasis on overall metabolism and energy levels.